About bonds between magnetic description of n-alkanes
and their critical parameters
SUE «Institute of Petroleum Refining and Petrochemistry, Ufa
Ufa state academy of economics and service, Ufa, Russia
E-mail: *****@***ru, *****@***com
Methods of mathematical simulation are increasingly spread in chemical technology, gradually ousting physical and chemical experiment. Considerable quantity of experimental data about physical-chemical properties (PCP) of individual hydrocarbons make it possible to model different technological processes about refining and petrochemistry employing modern additively-prop method and program product, like Hysys or Pro II, with sufficient effectiveness.
There are many disadvantages in this widespread method:
-PCP are calculated for simple systems,
-there is no explanation bond between different PCP for individual chemical compound or for difficult multi-component systems with unknown compound.
Thermo-physical properties of hydrocarbon systems are known very well. Much less attention is paid to their electro-magnetic properties. Relations between quantity of paramagnetic centers in multy-component organic systems of oil and petroleum product with such PCP like coking, energy of activation of viscous flow, and coloring behaviour in seed range of electromagnetic emission, were exposed in F. G. Unger`s and M. Yu. Dolomatov`s works and in many other works. Taking into account, that method of electronic absorptive spectroscopy found on interaction learning matter and electromagnetic radiation in specific range wave length, the relations between electromagnetic and other PCPs can be supposed. Accurate correlation between electronic description and the PCP of n-alkenes like molecular weight, temperature of ebullition, density and so on was found [5].
The aim of this work is development of the assessment method and prediction PCP of hydrocarbons and materials on their basis. The task is to expose interconnection character between fundamental physical-chemical and magnetic properties of n-alkenes.
References [6-8] were used in this work. After their analysis we can make a conclusion that methane is an exception from general series. Thus, it is necessary to investigate interconnection between basic physical-chemistry and magnetic properties of n-alkanes homologue C2-C10.
Examination of bond critical parameters between n-alkanes C2-C10 and its SMR shows that critical temperature is connected with magnetic properties of empirical exponential dependence Tcr=8·107·e-14,067·x with correlation coefficient R=0,99.
Critical pressure has logarithmic type of dependence from SMR: Pcr=494,45·Ln(x)+107,97 with correlation coefficient R=0,99.
Classical theory explains the heat properties of specific magnetic susceptibility on the basic statistical consideration of system parts (atoms, molecules or ions) having magnetic dipole moment and slightly relating with each other. Heat movement of particles is considered to prevents orientation of magnetic moment on the area.[9].
The conclusion based on dependence is that magnetic properties of n-alkanes have character of bond with critical properties like electronic characteristics.[10] The resulted character of relation between critical and magnetic properties of n-alkanes C2-C10 and result of previous work [1,5,10] allow to suppose the collective character of interaction of electrons in the substance.
So, analysis of bonds between different PCP of hydrocarbons reveals the cause of result equipment deviation in place with mathematical models based on straight measuring in laboratory or industrial term.
References:
1 F. G. Unger, L. N. Andreeva. Fundamental aspects of chemistry of oil. Nature of resins and asphaltenes. - Novosibirsk: Science, 1995. – 192 p.
2 M. Yu. Dolomatov, L. A. Dolomatova, V. V. Kartashova, G. R. Mykaeva and others. Analysis hydrocarbon systems and produce its treatment with method electronic spectroscopy on basic of correlation spectrum-properties //Materials of the 1-st international forum «Analitic and analysts» Voroneh, the 2-6 of June, 2003y. – 25 p.
3 G. U. Yarmuhametova. Development and use of method of appraisal physical-chemical property of oil and high-boiling fractions on color characteristics. – Abstr. Of Cand. Tekn. Scien. Diss. – Ufa: USPTU. - 2009. – 24 p.
4 M. Yu. Dolomatov. Chemical physics of multicomponent organic system. Part 1. Physical-chemical theory of difficult organic and petrochemical systems. – Ufa: UPPH AS RB, DTR, 2000. – 124 p.
5 S. V. Dezorsev, M. Yu. Dolomatov, A. R. Habirova. About connection of the first ionization potential of n-alkanes with their physical-chemical properties //Bashkirskii chimicheskii journal. – 2011. – T.18, №1. – P. 83-85.
6 Physical-chemical properties of individual hydrocarbons /Under the editorial staff of professor V. M. Tatevsky/ - M.: Gostoptehizdat, 1960. – 412 p.
7 S. A. Ahmetov, A. R. Gaisina. Modelling and engineering account of physical-chemical properties of hydrocarbon systems: studies, manual. – SPb.: Subsoil, 2010. – 128 p.
8 U. V. Ergin, K. S. Yarullin. Magnetic properties of oil. – M.: Scientist. – 1979. -200 p.
9 V. M. Yavorsky, A. A. Detlaf. Reference book of physics for engineers and students of IHE. – M.: Science, 1968. – 940 p.
10 S. V. Dezortsev, M. Yu. Dolomatov, S. A. Shutkova, D. O. Shulyakovskaya. The Connection Between Electronic Structure and Physical-Chemical Properties of n-alkanes (Report I) // XVIII International Conference on Chemical Thermodynamics in Russia, Samara, Russian Federation, October 3-7, 2011, Vol. 1, p. 71-73.
УДК:
, ,
выход продуктов деасфальтизации гудрона в зависимости от физико-химических свойств н-алканов
ГУП «Институт нефтехимпереработки РБ»,г. Уфа
Уфимская государственная академия экономики и сервиса, г. Уфа
E-mail: *****@***ru, *****@***com
Для углубления переработки нефти необходимо в разы снизить содержание металлов, серы и коксообразующих веществ в составе ее тяжелых остатков. Одним из возможных решений в промышленном масштабе является хорошо известный процесс деасфальтизации гудрона (или нефти) легкими углеводородными растворителями. Однако, имеющиеся варианты пропановой и пропан-бутановой деасфальтизации отличаются низкими выходами деасфальтизата и высокими давлениями в процессе эксплуатации (до 35-40 ати). В связи с этим становится актуальным возврат к процессам деасфальтизации гудрона легким бензином (Добен), который эффективно снижает содержание металлов и коксообразующих веществ. Преимуществом является более высокий выход деасфальтизата по сравнению с пропановым и бутановым вариантами и более низкие давления в реакторе.
Целью работы является изучение материального баланса процесса деасфальтизации гудрона н-алканами бензиновой фракции в лабораторных условиях (температура 200С, давление атмосферное) в зависимости от физико-химических свойств растворителя.
В качестве объекта исследования выбран прямогонный гудрон западно-сибирской нефти, являющийся сырьем установки висбрекинга (Ткип>400 0С). Выделение асфальто-смолистых веществ (АСВ) выполнено по способу Гольде. Для осаждения АСВ использовали бензол, н-пентан, н-гексан, н-гептан и петролейный эфир фракции 40-700С. Чистота всех растворителей не ниже квалификации ч. д.а. Бензольный раствор гудрона перед осаждением подвергали фильтрованию через обеззоленный бумажный фильтр.
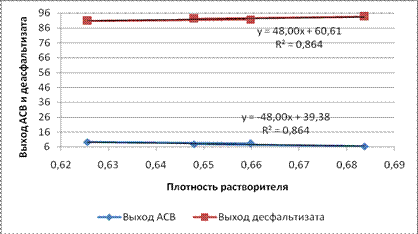
Рисунок 1 - Зависимость выхода АСВ и деасфальтизата от плотности растворителя
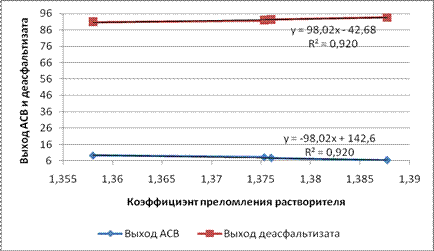
Рисунок 2 - Зависимость выхода АСВ и деасфальтизата от коэффициента преломления растворителя
Результаты экспериментов приведены на диаграммах (рис. 1 и 2). Корреляционные зависимости выхода АСВ и деасфальтизата от средней числовой молекулярной массы и нормальной температуры кипения н-алканов С5-С7 адекватно описываются линейными зависимостями вида y=a·x+b с коэффициентом корреляции R=0,93 и 0,96. Коэффициенты полученных эмпирических зависимостей приведены в таблице.
Таблица – Коэффициенты эмпирических зависимостей связи выхода продуктов деасфальтизации и параметров растворителя
Продукт | Уравнение вида y=a·x+b | |||||
Плотность растворителя, г/см3 | Коэффициент преломления растворителя | |||||
a, (г/см3)-1 | b, % масс. | Коэффициент корреляции | a | b, % масс. | Коэффициент корреляции | |
АСВ | -48 | 39,38 | ~0,93 | -98,02 | 142,6 | 0,96 |
Деасфальтизат | 48 | 60,61 | ~0,93 | 98,02 | -42,68 | 0,96 |
Таким образом, в процессе деасфальтизации выход асфальто-смолистого остатка и деасфальтизата линейно зависит от физико-химических свойств н-алканов, входящих в состав бензиновых фракций. Полученные результаты способствуют уточнению математической модели процесса. Коэффициенты a при соответствующем физико-химическом параметре в случае АСВ и деасфальтизата имеют одинаковые абсолютные значения.
УДК: 665.733:543.6
, ,
О связи критических параметров н-алканов и алкил-ароматических углеводородов с удельной магнитной восприимчивостью
ГУП «Институт нефтехимпереработки РБ», г. Уфа
Уфимская государственная академия экономики и сервиса, г. Уфа
E-mail: *****@***ru, *****@***com
Одной из основных проблем моделирования физико-химических свойств (ФХС) углеводородных систем является различие свойств между углеводородами разных групп (разных гомологических рядов) с одинаковым числом атомов углерода, например, в ряду н-гексан – изо-гексан – циклогексан – гексен – бензол. При этом наиболее резко различаются свойства н-алканов и ароматических углеводородов. , и показана возможность моделирования ФХС н-алканов на основе корреляций с их удельной магнитной восприимчивостью (УМВ).

|
Из за большого объема этот материал размещен на нескольких страницах:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 |





