VII. Answer the following questions.
1. Is health care in Belarus free of charge?
2. What is the primary aim of the state health care policy of the Republic of Belarus?
3. Special attention is paid to the maternity and childhood protection, isn’t it?
4. What is the characteristic feature of health care in our country?
5. What are the major principles of our health service?
6. What is the life-span (mortality rate, birth rate) of Belarusian people?
7. Where may a sick person receive treatment?
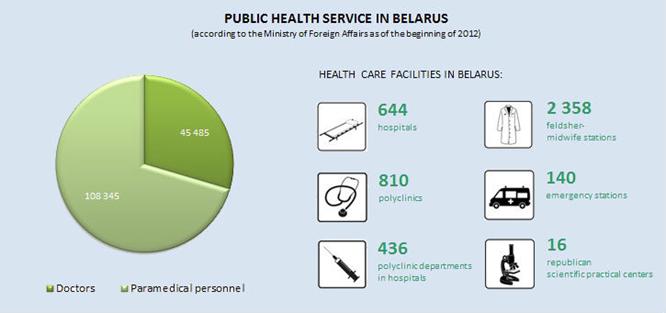
8. How many hospitals (polyclinics) are there in the Republic of Belarus?
9. Where is the primary medical care provided?
10. What do you know about the work of a district doctor?
11. What do people do in case of an emergency condition?
12. How is secondary care organized in the Republic?
13. What is the role of health resort treatment in the health care system?
14. Are there any specialized health centers in Belarus?
15. What are the main problems facing medical science in our country?
16. Into what problems are scientists doing research?
VIII. Agree or disagree with the statements using the following phrases: Yes, I agree that... / It is true that... / Yes, I think that … Or: I don't think that is correct... / I can't agree with the fact that... / No, I don't think you are right...
1. Prevention of diseases is the main principle of health care in our country. 2. There are some private clinics in Belarus which are not financed by the state. 3. Large industrial enterprises do not provide medical care for the workers. 4. Periodic screening is restricted only to ТВ patients and does not involve patients with hypertension, coronary heart diseases, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. 5. The primary medical care is provided by hospitals. 6. Most hospitals have the following major departments: surgery, obstetrics and gynecology, pediatrics and therapeutics department. 6. The average length of stay of a patient in a hospital is 15 days. 7. Health resorts provide the whole range of modern physiatrists’ services.
IX. Using the following phrases speak about
a) primary medical care in Belarus:
be provided by, routine health checks, health education, immunization, sickness certification, home visits, antenatal and obstetric care, to have a range of specialists, ambulant patients, district doctor, to be on call, to visit patients in their homes.
b) rendering emergency ambulance service:
emergency medical service, to deal with urgent cases, free of charge, to dial 103 for the doctor to come, blood-transfusion equipment, cases of myocardial infarction, acute heart disease, to handle any emergency, to give emergent treatment.
c) secondary care in Belarus:
to be organized, territorial basis, designated hospital, district hospitals, to provide common services, a wide range of specialties, complex cases, to be referred to the regional hospital.
d) health resort treatment in Belarus:
medical rehabilitation system, health resorts, to specialize in, to provide the whole range of modern physiatrists’ services, to visit for recreation and medical treatment, to offer services to foreigners.
 X. Role play the dialogue.
X. Role play the dialogue.
Doctor: Well, Mary, other than that rash (сыпь), you’re in great health.
Patient: Okay, Doctor. What should I do about it?
Doctor: I want you to go to dermatology. Make an appointment for them to look at it.
Patient: Where is that department?
Doctor: It’s on the 3rd floor. Turn right when you pass the radiology department.
Patient: Great, I’ll head up there now.
Doctor: But first, you should refill your prescription at the pharmacy.
Patient: The pharmacy is downstairs, right?
Doctor: Yes, next to the emergency room.
XI. Speak about Health Care System in Belarus using the following plan.
1. Main principles of Belarusian health care system.
2. The primary medical care.
3. The secondary medical care.
4. Health resort treatment.
5. Research and practical centers.
6. Fields of medical research.
Self check |
XII. Translate into English using words from Active and Reference Vocabulary.
1. Все граждане Республики Беларусь имеют право на высококвалифицированную медицинскую помощь.
2. Каждый гражданин нашей страны может получить медицинскую помощь бесплатно.
3. Платные медицинские услуги включают в себя оказание профилактической, лечебно-диагностической, реабилитационной и зубопротезной помощи.
4. Профилактика позволяет предупредить и вовремя излечить сердечно-сосудистые, онкологические и другие заболевания.
5. Школьники регулярно проходят профилактические медицинские осмотры.
6. Увеличение продолжительности жизни – это проблема, которой занимается геронтология.
7. Оказание медицинской помощи в республике Беларусь организовано по территориальному принципу.
8. Пациенты могут получить первичную медицинскую помощь в поликлинике.
9. Участковый врач работает 7 часов в неделю: 4 часа принимает пациентов в поликлинике и три часа посещает пациентов на дому.
10. В нашей стране есть поликлиники для детей и для взрослых.
11. Легче предупредить заболевание, чем лечить, не так ли?
12. Чтобы поехать в санаторий или дом отдыха нужно иметь путевку.
13. Кроме оплачиваемого декретного отпуска, женщина имеет право на ежемесячное пособие.
14. Люди с хроническими заболеваниями состоят на учете в поликлинике.
15. Новые методы лечения широко используются в медицине.
16. Средняя продолжительность стационарного лечения – 10 дней.
17. Я записался на прием к хирургу на среду на 10 часов утра.
18. Врач продлил мне больничный лист еще на одну неделю.
19. Вы можете получить лекарство по рецепту в любой государственной аптеке.
20. Научно-исследовательские институты разрабатывают новые методы лечения и работают над усовершенствованием медицинского оборудования.
21. Республиканские научно-практические центры внедряют новые технологии в диагностику и лечение заболеваний.
PART II
Text 2 |
I. Read and memorize the following word combinations. Translate the sentences.
1. natural population loss – естественная убыль населения
In 2002 the natural population loss reached its maximum level (–5.9) and it decreased to –2.8 in 2011.
2.programme-oriented planning – программно-целевое планирование
The programme-oriented planning in health care is a key mechanism to increase the efficiency of the branch.
3. restructuring of the branch – реструктурирование отрасли
Restructuring of the branch is carried out.
4.hospital-substituting technologies – стационар-замещающие технологии
Implementation of hospital-substituting technologies allows using hospital resources more efficiently.
5. evidence-based medicine – доказательная медицина
cost-effectiveness analysis – анализ экономической эффективности, анализ соотношения между затратами и эффективностью
More than 1000 clinical protocols grounded on evidence-based medicine and cost-effectiveness analysis of medical care have been introduced.
6. stipulate – предусматривать
Improvement of the demographic situation in the country is stipulated in the Directions of the Strategic Development of Health Care of the Republic of Belarus for 2011–2015.

II. Read and translate the text.
Achievements of the Health Care System of the Republic of Belarus (1991-2011)
 During the period 1991–2011 the infant mortality rate decreased more then 3-fold (up to 3.9 per 1000 live births) and it is the lowest one in the CIS countries.
During the period 1991–2011 the infant mortality rate decreased more then 3-fold (up to 3.9 per 1000 live births) and it is the lowest one in the CIS countries.
In 2002 the natural population loss reached its maximum level (–5.9) and it decreased to –2.8 in 2011.
There is a positive tendency to an increase in life expectancy (70.6 years in 2011).
Since 2000, the process of health care reforming in Belarus has become systemic. The introduction of the state social standards which ensure the realization of the citizens’ social rights stipulated in the Constitution of the Republic of Belarus, is a distinctive feature of the national health care system.
The programme-oriented planning in health care as a key mechanism to increase the efficiency of the branch has been introduced. The following state programmes are aimed at health promotion, reduction of morbidity and mortality: National Programme of Demographic Security of the Republic of Belarus for 2011–2015, State Integrated Programme on Cancer Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment for 2010–2014, State Programme "Tuberculosis" for 2010–2014, State Programme of HIV-Infection Prevention for 2011-2015, State Program on Overcoming the Consequences of the Chernobyl Accident for 2011–2015 and the Period to 2020, State Programme “Cardiology” for 2011–2015, etc.

|
Из за большого объема этот материал размещен на нескольких страницах:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |





